Are you worried about seeing blood in the sink while brushing your teeth? It is due to bleeding from your gums, which may be simply because of harsh brushing or something underlying severe disease.
Did you know your gums are just as important as your teeth?
Many people ask me how to care for their teeth to maintain good oral hygiene, forgetting about gum health. While caring for your teeth is essential, remember the importance of gum health in maintaining complete oral hygiene.
In this article, you will gain complete knowledge of bleeding gums: What causes them to bleed, the different ways they can be treated, and most importantly, how we can prevent this issue from occurring in the first place.
What do Bleeding Gums mean?
Bleeding gums can indicate that you have or may develop gum disease. It is often associated with gum disease, a common issue many face. The leading cause for this is the buildup of plaque or tartar along the gum line. This condition causes discomfort and can lead to more serious oral health problems, including bad breath, tooth removal, and gum disease.
Why do my gums bleed when I brush my teeth?
Bleeding gums can be a sign of several dental and overall health issues, so it’s essential to understand the possible causes and when to seek medical advice. Here, I listed 10 possible causes of bleeding gums.
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
The most important factor of gum health is proper oral hygiene. When plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, isn’t removed effectively, it can harden into tartar. This buildup irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and bleeding. Regular brushing and flossing are essential to remove plaque and prevent this progression.
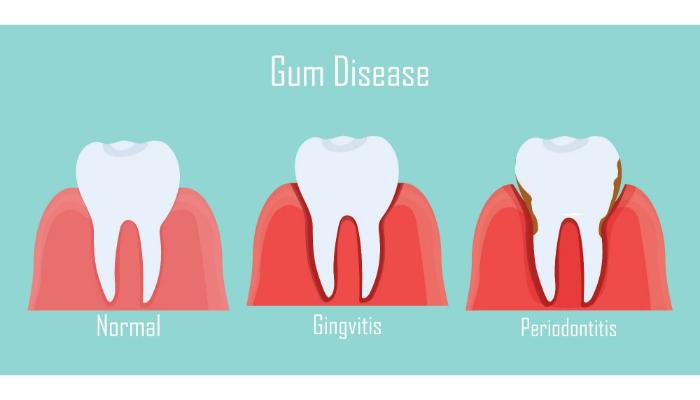
2. Gingivitis
Bleeding gums are a sign of gingivitis. This is the earliest stage of gum disease, caused by plaque building up at the gum line. If not removed through daily brushing and flossing, it can lead to inflamed, tender gums and be prone to bleeding.
3. Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it progresses into Periodontitis. Periodontal disease is a more advanced form of gum disease that affects the gums, jawbones, and tissues supporting teeth. It can lead to teeth loosening or falling out if not treated.
4. Vitamin deficiency
A lack of essential vitamins, such as C and K, can impair gum health and lead to bleeding. These vitamins are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the gums and aiding in the healing process. Check your vitamin- C and K levels if you have bleeding gums that aren’t caused by improper dental care.
5. Pregnancy
Pregnancy is associated with hormonal changes. These hormonal changes can enhance the blood flow to the gum tissue, and gums become more sensitive, swollen, and prone to bleeding during brushing or flossing. This condition is called Pregnancy gingivitis.
6. Medications
Some medications can cause gum sensitivity or bleeding gums. Blood thinners can increase the risk of bleeding gums by reducing blood’s ability to clot, resulting in easier bleeding. Medications that reduce saliva flow can also allow bacteria to flourish, worsening gum problems.
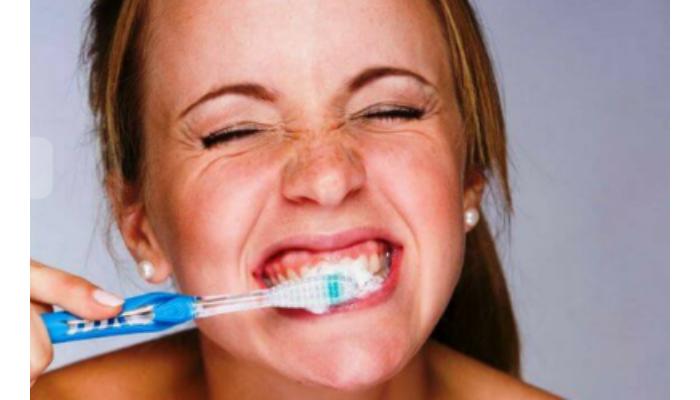
7. Brushing Too Hard
Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause your gums to bleed. Aggressive brushing can damage the gum tissue, causing bleeding and receding gums. Follow a proper brushing technique, use a soft-bristled toothbrush, and be gentle.

8. Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for many oral health issues, including bleeding gums. It causes the narrowing of the blood vessels, which reduces blood flow to the gums and can weaken their natural ability to repair, making them more susceptible to infections and bleeding. People who smoke are at increased risk of developing gum disease.
9. Wearing ill-fitting dentures
Wearing ill-fitting dentures can rub against the gums, causing swollen gums, inflamed gums, and prone to bleeding. If you wear dentures, brushing and cleaning your teeth is especially important to prevent plaque buildup and inflammation of the gums.
10. Systemic Diseases
Systemic diseases affect the entire body, can profoundly impact oral health, and can be the cause of bleeding gums. The relationship between systemic health and oral health is bidirectional; systemic diseases can lead to oral health problems, and poor oral health can worsen systemic conditions.
Below are some systemic diseases that are known to cause bleeding gums:
- Diabetes
- Leukemia
- Haemophilia
- HIV/AIDS
- Anaemia
- Herpes
- Thrombocytopenia
- Stress
Treatment of Bleeding Gums
Treating bleeding gums is crucial not only for maintaining oral health but also for ensuring overall well-being. As a professional dentist, I recommend a complete approach to treating bleeding gums, focusing on professional dental care and good dental hygiene practices at home. Here’s a detailed guide on how to treat bleeding gums effectively
At Home Care:
1. Proper Brushing and Flossing: Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once daily are key. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle motions to avoid irritating your gums further. Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles between teeth and along the gumline.
2. Antimicrobial Mouthwash: An antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash can help reduce plaque and prevent gingivitis, reducing gum bleeding.
3. Rinse your mouth with warm saltwater: Rinse your mouth with salt water can help reduce bacteria and speed up healing times. Swish the salt rinse around the mouth to cleanse the area, then spit the liquid out. Repeat this several times a day or according to instructions from your dentist.
4. Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially Vitamin C and calcium, can strengthen gum tissue and teeth. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks that can contribute to plaque buildup.
5. Quit Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease. Quitting smoking can improve oral health significantly and reduce the risk of bleeding gums.
6. Stress Management: Stress can affect your ability to fight infections, including gum disease. Finding ways to manage stress that can improve your oral health and reduce bleeding gums.
Professional Dental Care:
1. Dental Cleaning: Regular dental cleanings are essential. During these visits, the dentist will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth, especially from areas hard to reach with a toothbrush. This process, known as scaling, helps reduce gum inflammation and bleeding.
2. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing): For more advanced gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be necessary. This involves cleaning below the gumline and smoothing the roots of your teeth to help the gums reattach, reducing pocket depths and encouraging healing.
3. Medications: Sometimes, your dentist might recommend antibiotics to help control bacterial infection causing gum inflammation. Antimicrobial Mouthwashes can also be prescribed to reduce bacteria in the mouth.
4. Adjustment of Dental Appliances: If ill-fitting dentures or other dental appliances contribute to gum irritation and bleeding, your dentist can adjust or replace them to improve fit and comfort.
When to See a Dentist
If you notice persistent gum bleeding, swelling, or pain, you must immediately see a dentist or Periodontist (gum specialist). These could be signs of gum disease or other oral health issues that require professional treatment. Additionally, at least twice a year, regular dental check-ups can help avoid treatments like dental fillings, Root Canal Treatment, and tooth extraction followed by replacement.
How to Prevent Bleeding Gums
People can often avoid and prevent gums from bleeding by:
- Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss daily.
- Regular dental check-ups and cleaning.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for essential vitamins and minerals.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and flush out bacteria.
- Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen teeth and protect gums.
- Consider using an antibacterial mouthwash as part of your routine.
- Manage stress, as it can contribute to inflammation and gum problems.
Conclusion: Healthy Gums- Healthy Life.
Bleeding gums are a sign that your oral health needs attention. You can stop bleeding gums with the right care, including proper hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, dental treatments, and a healthy lifestyle. Remember, maintaining healthy gums is not just about protecting your smile; it’s about safeguarding your overall health and well-being. If you experience persistent bleeding from the gums, seeking professional dental care is crucial. With the proper approach, bleeding gums can be effectively managed, ensuring your oral health is on the right track.
If you have any queries, please book an appointment with me.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bleeding gums are often a sign of gum inflammation, usually caused by plaque buildup along the gumline. Improper or aggressive brushing and flossing can damage your gums and cause them to bleed.
To stop your gums from bleeding, maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash. Also, visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. Addressing any underlying health issues is also crucial.
No, it would be best if you did not stop brushing or flossing. Instead, ensure you are using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle techniques. Keep your gums healthy by maintaining proper dental hygiene practices.
Yes, in many cases, bleeding from the gums is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care. Early intervention is key to preventing the progression into more severe gum disease.
Yes, it is a common and early symptom of gum disease. While bleeding gums are often a sign of gum disease, they can also indicate other health concerns.
